What is RF Interference?
Learn about radio frequency interference, how to detect it, potential causes, and how to stop it.
Radio frequency interference (RFI) is the presence of unwanted signals or electrical energy that detrimentally impact a radio communication system. The causes of RFI interference include external, naturally occurring sources like thunderstorms and static electricity, as well as man-made sources created through out-of-band transmissions, radiation from network antennas and cabling, and the proximity of adjacent networks operating on overlapping frequencies. RF interference dates to the earliest telegraph and radio communication, when unwanted humming, static, or service interruptions were caused by external radio waves or electrical activity.
The wide variety of interference sources and the need for specialized interference test and measurement equipment make it important to distinguish between interference types. RF signal interference sources fall within the broad sub-categories of intentional and unintentional radiators of RF energy. Both types of RF interference can contribute to the noise floor, which makes interference analysis more challenging.
What causes radio frequency interference?
- Intentional interference is produced by everyday objects like portable radios, baby monitors, and cell phones as well as inadequate RF designs or cell tower co-siting practices that impact a receiver’s sensitivity. Radio frequency interference examples in this category also include malicious interference signal types and practices such as jamming, or powering down cell phones during airplane takeoff and landing to protect communication systems.
- Unintentional interference is generated by devices that produce RF energy as a byproduct of their operation, which allows radiated energy to be “leaked” out to nearby areas. Potential sources of unintentional interference include computer monitors, ovens, and electrical motors. Products which contain a digital timing component (oscillator), including laptop computers and tablets, can also create unintentional interference.
Detecting RF interference begins with recognizing the symptoms and analyzing the data. A review of system alarms, KPIs, and logs can often reveal whether a weak signal, elevated receive noise floor, or high bit error rate could be due to a hardware failure or configuration issue, rather than interference.
Locating and diagnosing the wide range of RFI radio frequency interference sources quickly and accurately requires a versatile test and measurement tool kit. RF interference hunting practices include the use of spectrum analyzers at the cell site to determine whether the interference is being generated internally or externally and to:
- Analyze any interference signals within the receiver’s bandwidth that are not filtered out.
- Characterize the noise floor to determine whether intermittent noise is compromising signal quality.
- Use a real time spectrum analyzer with continuously overlapping data capture to prevent intermittent or transient signals from being missed.
- Use a persistent spectrum display to allow the rapid data collection of real time spectrum analysis to be presented graphically, using color or brightness to signify the probability of signals appearing at a given frequency.
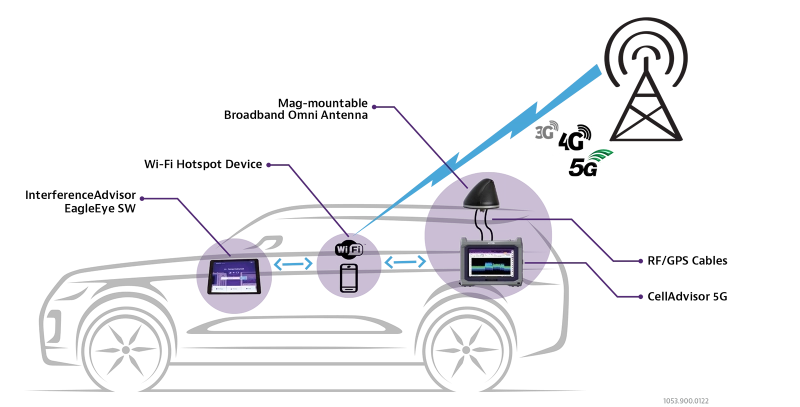
Once the nature and intensity of the interference has been characterized through a network test and on-site analysis, the physical position of the source must be identified. The VIAVI InterferenceAdvisor is an intuitive mobile solution that allows an RF engineer or technician to locate an interference source with minimal effort.
A VIAVI OneAdvisor 800 Wireless portable test device connected to a broadband Omni-antenna collects and analyzes signal interference data in transit. Fully automated EagleEye™ software running on a cable-free Android tablet then provides visual and voice prompts to guide investigators to the most probable area of interference origin, saving valuable troubleshooting time. The InterferenceAdvisor system also features gated sweep control and display for time division duplex (TDD) interference frequency hunting.
After the geographic area associated with the interference source has been narrowed down, the VIAVI AntennaAdvisor can be used to perform radial signal analysis and generate intersection vectors to triangulate the precise location of unwanted interference. Working in conjunction with the powerful real time spectrum analysis capabilities of the OneAdvisor 800 Wireless, rogue RF emission sources can be diagnosed, located, and eliminated quickly.

How to Measure Interference
Measuring interference accurately is the key to correctly diagnosing the type, source, and probable cause. Each wireless communication technology operates within an expected bandwidth and noise power level, measured in dBm. Any type of interference can affect the noise level, making it harder for the RF network to transmit efficiently or maintain adequate coverage at the edge of the network.
- Low-level signal measurement is essential for interference hunting and is directly impacted by the spectrum analyzer settings. Utilizing a low noise/high gain preamplifier, narrowing the resolution bandwidth (RBW) of the RBW filter, and minimizing the input attenuation can improve sensitivity considerably. The dynamic range of the RF signal analyzer, specified in dB, is also important for interference hunting applications because the expected and unwanted RF signals are best evaluated side by side.
- Wireless networks that continually exhibit spikes greater than -60 dBm above the noise floor or constant amplitudes greater than -80 dBm within the operating band of the spectrum are probably experiencing some form of RF interference. Each source of interference produces a unique signature that experienced RF engineers and technicians use to determine the most probable root cause(s). Spectrum analysis overlayed with network test data such as throughput or BER can be used to quantify the impact of interference on performance.
The broad categories of intentional and unintentional interference frame a growing list of potential interference causes. Advanced signal duplexing methods and increasingly crowded airwaves have created new RF interference sources requiring innovative test and prevention methods.
Passive Intermodulation (PIM)
Increased traffic within the finite RF spectrum has inevitably led to higher signal density. Multiband operation has helped to alleviate this bottleneck. However, a condition known as signal interference can occur when multi-frequency RF signals contact corroded hardware or joints between dissimilar metals on or around the cell tower.
The resulting passive intermodulation (PIM) causes signals from separate wireless communication sources to be mixed. This can impact mobile networks by lowering the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), increasing the bit error rate (BER), and decreasing throughput. The addition of frequency bands and carriers to support the 5G rollout has increased the opportunities for crossband PIM.
Co-Channel Interference
Another interference category that is symptomatic of congestion as operators share and compete for bandwidth is known as co-channel interference (CCI). As the name implies, this problem occurs when multiple signals are present over the same channel. Overlap in cellular coverage patterns can lead to co-channel or on-channel interference, although most cell phones can process at least five simultaneous signal paths without any issues.
- Time division duplex (TDD) enables uplink and downlink transmissions to operate over the same frequency on 5G networks. Interference can occur when stringent timing and synchronization requirements are not met. With more channels being shared, detailed frequency planning in network operations is necessary to prevent co-channel interference from disrupting the user experience.
- Adjacent channel interference (ACI) occurs when neighboring frequencies “bleed” into one another due to improper filtering or tuning. Appropriate guard banding between adjacent channels can mitigate this issue and prevent the loss of bandwidth or noise caused by adjacent interfering signals. The potential interference between aircraft radio altimeters and 5G networks operating on nearby C-band (3.7 – 3.98 GHz) frequencies is an example of an ACI risk.
How Can You Stop Interference?
To paraphrase a familiar catchphrase from the world of sports: You cannot stop RF interference, you can only hope to contain it. Learning how to stop radio interference begins with a realization that there will always be naturally occurring, unintentional, and unexpected forms of interference. The most successful RFI interference reduction strategies use a multi-faceted approach that includes:
- Cell tower deployment planning to establish maintenance practices that minimize PIM and optimize the TDD frame structure between collocated networks to prevent inter-cell interference.
- Continuous monitoring of network transmissions for instances of ongoing or intermittent interference, increased BER, and other forms of signal degradation that should be addressed in real time.
- Shielding, re-routing, or filtering potential sources of unintentional interference like cabling, powered equipment, and lighting.
Effective testing for RF interference should account for all intentional and unintentional interference sources, utilize the expertise of experienced RF engineers and technicians, and deploy a combination of interference test processes including:
- Site surveys to characterize signal strength and quality at various locations and identify previously undetected interference sources.
- Spectrum analysis to identify sources of interference in the frequency band of interest and baseline system noise.
- Over-the-air frame format testing for 5G networks using the OneAdvisor 800 Wireless to validate the TDD frame formats of multiple operators.
- Interference hunting to proactively seek out, characterize, and eliminate interference sources before they impact QoE.
What is Interference Hunting?
Interference hunting is the process of locating, identifying, and eliminating unwanted sources of interference that degrade the quality of wireless reception on the receiving end. As more devices and users are introduced within the limited RF spectrum, minimizing the impact of interference becomes more challenging. Interference hunting tools and practices put advanced technology to work to reduce the impact on network capacity and subscriber QoE.
Interference issues in wireless networks can result in a higher noise floor on the received channel and a lower signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) that degrades signal quality. Mobile users near a source of interference will experience lower data throughput, limited range, more dropped calls, or poor voice quality.
5G Interference
5G introduces new interference hunting challenges through cell densification and the range limitations of the millimeter wave (mmWave). 5G network operations also leverage frequency division duplex (FDD), dynamic TDD, and other frequency sharing options that can increase the potential for co-channel interference.
- Interference hunting for 5G requires real time spectrum analysis to capture complex interference signals overlapping the 5G NR signal. Exceptional bandwidth and dynamic range are needed for 5G beam and interference analysis in the FR1 (sub-6GHz) and FR2 (mmWave) frequency ranges. Persistent display is a useful feature for distinguishing 5G uplink interference signals that traditional swept tuned methods can miss.
- RF over CPRI (RFoCPRI) technology uses the CPRI interface to verify control signals and extract user plane traffic or RF (IQ) data. Interference signals on mobile devices (uplink) and radio performance data (downlink) can be monitored and analyzed from the ground. This simplifies 5G interference troubleshooting and minimizes cell tower climbs.