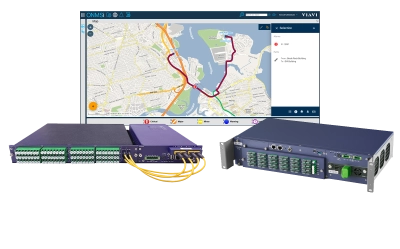
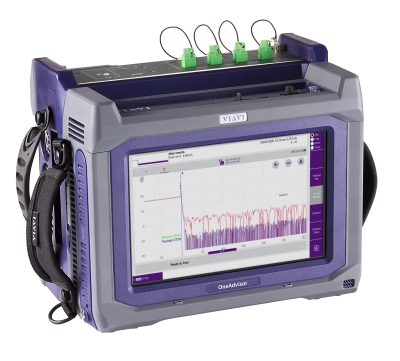
光ファイバーセンシング
業界トップのモジュール式光ファイバーセンサ、ポータブル型およびラックマウントオプション
VIAVI は、ポータブル型 OneAdvisor 光ファイバーセンシング、またはリモートファイバーテストおよびモニタリング用のラックに収容可能なファイバーテストヘッド光ファイバーセンシングで、ブリルアン OTDR、ラマン OTDR、レイリー OTDR を使用して、光損失、温度、温度と歪み、または音響振動を測定する分布型温度センシング(DTS)、分布型温度および歪み同時センシング(DTSS)、分布型音響センシング(DAS)ソリューションを提供します。
製品
-

FTH-DAS
市場で最も汎用性の高い音響センシングソリューションで、重要なインフラを外部の脅威から守り、パイプラインの漏れを監視
-

FTH-DTSS
市場で最も汎用的な光ファイバーセンシングソリューションを使用して、電源ケーブル、パイプライン、通信ケーブルの温度および歪みを監視します。
-

FTH-DTS
市場で最も汎用的な光ファイバーセンシングソリューションを使用して、電源ケーブル、パイプライン、通信ケーブルの温度を監視します。
-

ONMSi 遠隔ファイバーテストシステム(RFTS)
コア、メトロ、アクセス、および FTTH ネットワーク用の ONMSi 光ネットワーク管理システム
-

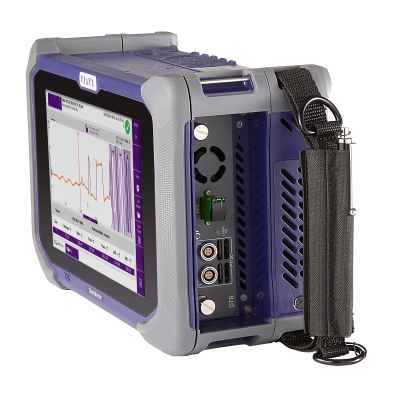
OneAdvisor 800 DTS
比類ないポータブル型ソリューションで、フィールドに分散型温度センシングテクノロジーをフィールドにもたらします。市場で最も多機能な光ファイバーセンシングソリューションを使用して、クリティカルなインフラを監査、チェック、保守します。...
-

OneAdvisor 1000 DTSS
比類ないポータブル型ソリューションで、フィールドに分布型温度および歪みセンシングテクノロジーをフィールドにもたらします。市場で最も多機能な光ファイバーセンシングソリューションを使用して、クリティカルなインフラを監査、チェック、...
VIAVI はどのような種類の光ファイバーセンシングインテロゲーターを提供していますか?
VIAVI ファイバーセンシングポートフォリオには以下が含まれます。
- ラマン OTDR 技術に基づく DTS (Distributed Temperature Sensing、温度分布測定)
- ブリルアン OTDR 技術に基づく DTSS (Distributed Temperature and Strain Sensing、温度・歪み分布測定)
- コヒーレントレイリー後方散乱技術に基づく DAS(分布型音響センシング)
光歪みゲージとしても知られる光ファイバー歪みセンサーは、特殊な OTDR(光時間領域反射率計)を使用した歪み分布測定として知られるプロセスによって、歪みを検出または感知するために使用される光ファイバーです。これらのセンサーは、センサー内の光の変化を測定して、グラスファイバーに沿った領域が伸びてガラスに変化が生じ、最終的に過度の歪みがかかって破損するまでファイバーにかかる歪みを検出するために使用されます。従来の電気歪みゲージとは異なり、パッシブ光ファイバー歪みセンサーは常時通電する必要がなく、電気歪みゲージシステムでノイズとして発生する電磁干渉の影響を受けません。このようなノイズがあれば、測定値が判読できなくなる可能性があります。
この利点により、操作コストが低くなり、歪みの変化に対する並外れた感度を備えた信頼性の高い測定デバイスとして、多くの過酷な物理環境で使用できます。光パルスをファイバーに送信してガラスの歪みを測定することで歪みを検出します。これらのタイプの測定は、フィールド測定に出向いた際にポータブル型 DTSS(温度・歪み分布測定センサー)OTDR を使用して定期的に行うことも、常設のラックマウント式 DTSS OTDR を使用して自動化されたルーチンで行うこともできます。光ファイバーは軽量で安価であり、ファイバーをテスト対象のデバイスの複数の場所に取り付けることで完全なカバレッジを実現できます。
光ファイバー歪みセンサを使用すると、パイプライン沿い、通信ケーブル上、地中、橋沿い、大型風車などのさまざまな場所で歪みを感知し、インフラや人命の安全を確保し、環境被害を防ぐことができます。すべての音響測定プロセスでは、光ファイバー歪みセンサの設置時に歪みのベースラインを確立し、時間の経過に伴う変化を測定します。これにより、指定された許容しきい値を超えた場合に自動アラームがトリガーされてリスクを通知できるようになります。
光ファイバー音響センサーは、高度な光ファイバーセンシング技術です。特定のポイントで測定する従来のセンサーとは異なり、分布型音響センシング(DAS)は光ファイバーケーブルの全長を連続的に監視します。光ファイバー自体が分布型センシングエレメントとなり、重要インフラ周辺の振動障害を長距離にわたって検知し、情報を取得することができます。
DTS または DTSS 機能を備えた VIAVI OneAdvisor 800/1000 プラットホームなどのポータブル型を使用することで、作業者はフィールドに出て、ファイバーのフィールド測定を行うことができます。あるいは、ONMSi および DTS または DTSS 機能を備えたラックマウント型ファイバーテストヘッド(FTH)を使用することで、NOC は当初の基準トレースから変化があった場合に警告が発せられるように設定した定期的なトレースを使用してファイバーをリモート監視することができます。
音響センシング機能(DAS)を備えた VIAVI ファイバーテストヘッドのようなラックマウント型ソリューションを使用することで、パイプラインのオーナー/オペレータや送電システムオペレータ(TSO)などは、リアルタイム監視およびアラームソリューションを導入し、人、トラック、機械的または手動による掘削など、資産に対して脅威となる可能性のある振動障害を検出、識別、位置特定、および警告することができます。
光ファイバーセンシングは、豊富なデータポイントソースとして、導入や使用にかかる費用や労力がはるかに少なくて済みます。ケーブル内のファイバーが分布型センサを形成しており、その材料は低価格、軽量、しかも被試験物への接続または組み込みが容易にできます。
ファイバーは高信頼性の分布型センサで、データを取得するために定電流を必要とせず、電磁波および高周波の干渉を受けません。従来、歪みや温度データを取得するためのメインデータソースは、重い有線電動センサで、導入に非常に手間がかかっていました。
電気機械式センサは外れ落ちる可能性があり、侵入的でコストが法外に高く、電源を必要とします。電源がない、または腐食、振動、EMI の問題がある場所では実用的ではありません。電気および無線ノイズのイングレスやイーグレスにより測定データが歪みます。安全性監視を必要とするブリッジはコスト効率の良い光ファイバーセンサ監視に対して最適で、ファイバーをブリッジに組み込んだり遡及的に接続したりしても、ブリッジが実際に故障する前に歪みや故障のリスクを検出できます。ファイバーをひどく曲げない限り、ファイバーを正弦波形に実装して表面全体でより多くのデータが得られるようにします。ファイバーセンサの実装時にファイバーの多少の歪みが必要となる場合、OTDR はマイクロおよびマクロベンドを検出し、ファイバーの歪みと曲がりを最適化できます。
光ファイバーセンシングは、光時間領域反射率測定(OTDR)を使用して、音響、歪み、温度、光伝送特性など、ファイバーの動きや曲がり、破損を示す複数の種類のデータを提供することができます。このデータは、個別に断続的に置かれたセンサ場所に限らず、ファイバーの全長に渡り提供されます。たとえば、OTDR を用いてこれらの値を測定することで長いファイバー全長に渡るグラジエントによりどの部分で温度が変化したかがわかります。また、ファイバーの伸びの開始と終了点からどこに歪みがあるかを見ることもできます。通信では歪みを回避しなければならないため、これを測定することでネットワークを保護し、ケーブル歪みのプロアクティブな軽減と修理が可能になります。ブリッジを監視したい場合、ファイバーセンサ上の歪みはブリッジプレートの分離によるたるみ、沈み、応力などのブリッジの動きを示す可能性があります。
データセンター、原子力発電所、血液銀行の貯蔵施設など、特定の温度に保つことを必要とする建物全体を通しての温度測定を考慮してください。従来型の電気式温度センサは幾つかの場所に置かれ、定期的に個別点を読み取ります。電子式温度センサは高価で常時通電する必要があります。センサがない場合や、電源障害、極度な温度、または EMI 干渉などが原因でセンサが機能しない場合にはどうなるか? 温度が最適に管理されていないため、高温点または低温点が生じます。1 本または複数本のファイバーケーブル形状の光ファイバーセンサ網で建物全体を網羅し、連続場所で測定値を読み取れます。このファイバー網はより多くのデータポイントを提供するため、低価格にて高信頼性のより良いカバレッジが得られます。ファイバーセンサによる情報取得に必要なのはレーザー OTDR が放つ光パルスのみで、装置は 1 日以上電源が切れた場合はバッテリー駆動できます。
さらに、分布型音響センシング(DAS)は、センシングファイバー上で音の周波数と振動に関する情報を提供し、資産周辺の環境で発生している振動障害の連続的かつ動的なリアルタイム情報を提供します。これにより、脅威検知能力が強化され、セキュリティ境界の侵害から、計画外のネットワーク構築工事(手作業や機械による掘削など)、環境上の危険や事象まで、特定の外部脅威を迅速に検知し、位置を特定することができます。迅速に対応し、お客様の資産を保護するために必要な、脅威を特定し正確に示すための重要なインテリジェンスを提供します。
光ファイバーセンサの革新的なアプリケーションにはどのようなものがあるか?
通信ケーブルは世界中あらゆる場所の険しい過酷な環境の地下、海底、空中に敷設されており、氷、風、地動、侵食、波、破壊行為、人的過誤によりケーブルの歪みや破断が絶えず生じており、サービスの停止と低下の両方が生じています。ケーブルは誤って歪んで敷設されることがあります。過度に歪むと、破断のリスクが生じ、ケーブルの寿命は 35~40 年から最悪の場合は数か月まで著しく短縮されます。
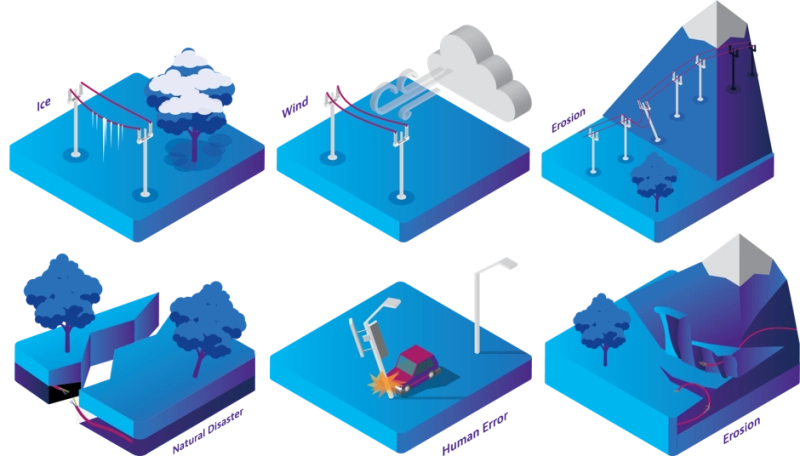

長距離回線および海底ケーブルはミッションクリティカルですが、険悪な天候、遠隔地、危険な地形の場合はサービスの提供が困難です。光ファイバーセンサを用いた分布型歪み検出により、ネットワークケーブル所有者は敷設時にファイバーテストを行い、その後のサービス提供中にダークファイバーの過度な歪みリスクや歪みの変化を監視することで破断を最小化できます。モーリタニアでは最近、海底ケーブルの破断が発生し、2 日間にわたり、ネットワーク全体がインターネットから切断されるという事象が起きました。これは、トロール船がアフリカ海岸からヨーロッパへのケーブルを海底から引き上げて破断したことが原因でした。このケーブルの歪みが監視されていれば、ケーブルが引き上げられていた間に破断する前に警告が発せられたはずです。破断してしまった場合にも、従来のレイリー OTDR は破断位置を 1m 以内の精度で特定するため、故障時間を短縮できたはずです。長距離回線および海底ケーブルはミッションクリティカルですが、険悪な天候、遠隔地、危険な地形の場合はサービスの提供が困難です。ファイバーをセンサーとして使用する分布型歪みセンシングにより、ネットワークケーブルの所有者は、敷設時にファイバーをテストし、ダークファイバーの過度の歪みリスクと使用中の歪みの変化を監視して破損を軽減することができます。分布型音響センシングにより、漁網や船のアンカーなど、接近する脅威を検知する監視が可能になります。モーリタニアでは最近、海底ケーブルの破断が発生し、2 日間にわたり、ネットワーク全体がインターネットから切断されるという事象が起きました。これは、トロール船がアフリカ海岸からヨーロッパへのケーブルを海底から引き上げて破断したことが原因でした。このケーブルの歪みや音響が監視されていたら、ケーブルが接近し、破断する前に引っ張られた時点でアラームが作動したことでしょう。破断してしまった場合にも、従来のレイリー OTDR は破断位置を 1m 以内の精度で特定するため、故障時間を短縮できたはずです。
過度な量の氷がついた空中ケーブルについて考えてみましょう。ネットワーク事業者はケーブルを監視し、そのようなネットワーク区間が見つかったら、作業者が氷を除去して過度な歪みを防ぐことができます。歪みが起きた後、ケーブルを MAT 公差測定値に照合してテストし、交換の優先順位を決めることができます。ポータブル型 DTSS 光ファイバーセンサ OTDR とラックマウント型ファイバーインテロゲーション OTDR が共に利用可能です。

ケーブル破断の最も一般的な原因は、建設のための掘削 (通称:バックホー減衰) です。破断位置が特定されると、多くの場合、その位置でケーブルをスプライスするか、コネクタを付けます。ただし、バックホーがケーブルを掘り出したとき、歪みにより破断位置の両側何メートルにも及びケーブルが損傷されているので、これは一時的な解決に過ぎません。

ケーブルを再敷設すると、再度破断するか、損傷しすぎて劣化しているために適切なサービスを提供できなくなる可能性があります。修理の繰り返しは高価で、再度サービス停止が起きることになる可能性があります。光ファイバーセンサ OTDR により破断部分の両側の歪み分布測定を行うことで、作業者は科学的な証拠を提供し、正確にどのケーブルセクションを交換する必要があるかを示すことができます。この証拠は、損傷コストを責任者に請求するために使用できます。これにより、その後の修理のための派遣および顧客へのサービス中断の繰り返し、ならびに歪みによる損傷のない良好なケーブルセクションの不要な修理を回避できます。
パイプラインは石油、化学物質、食品、廃棄物、水などの業界で、高価で腐食の可能性がある多様な物質を輸送します。パイプラインへの汚染物の流入や漏れあるいは盗難により壊滅的な問題が発生し得ます。パイプラインの監視はパイプラインに沿ったファイバーの温度と歪みを測定することで実現されます。ダムや堤防も同様に監視できます。ファイバーの温度や歪みまたは光反射特性の著しい変化があれば、漏れが疑われます。温度変化は漏れやタップを示し、歪みは予期されない動きによる破断のリスクを示し、従来の光反射によるレイリー散乱 OTDR 分析を用いて問題位置を 1m 以内の精度で特定できます。ラックマウント型 OTDR 監視ソリューションで歪み、温度、および光反射用の統合光インテロゲーションを使用して、パイプラインに接続したファイバーセンサを連続監視できます。光ファイバーセンサは正確な検出を行うことで、迅速にシャットダウン、検査、修理を行うことができます。
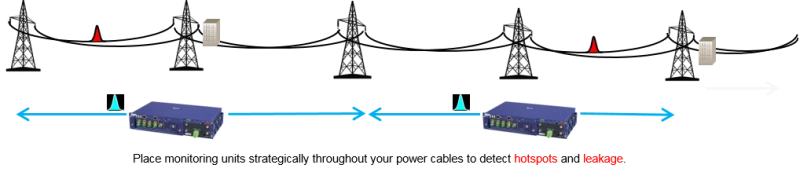
送電プラントでの電気ホットスポットは致命的な火災リスクおよびインフラ損害を引き起こします。その最近の例としては、米国カリフォルニア州で起きた電気ホットスポットまたは送電線の垂れ下がりによる森林火災の発火があります。人の命と家財が失われ、電力会社は訴訟や倒産に直面しています。
DTS 使用によるリモートファイバーセンシングがそのような問題の経済的な監視の唯一の方法で、そのような破滅的な結果のコストに比べはるかに低コストです。送電線をリモート監視するために送電線に沿ってファイバーを取り付けます。光ファイバーセンサシステムが温度上昇や送電線の垂れ下がりを示す歪みや曲がりを検出すると、警告が発せられます。レイリー OTDR 分析と併用すると、基準トレースを一定の定期トレースと比較することで、ファイバー位置の徐々のまたは急な移動があった場合にその正確な位置を特定できます。警告により、緊急電力遮断を引き起こし、送電線の調査を開始できます。光ファイバーセンサを用いたファイバー分析は EMI の影響を受けないため、この EMI の高い環境に最適なソースです。
光ファイバーセンシングおよびファイバー監視の詳細はこちら。
あらゆるステップでのサポート
VIAVIは、サポート、サービス、総合的なトレーニング、お客様が必要とするリソースを提供しています。これはすべて、お客様のVIAVIへの投資価値を最大化するために当社が日頃より行っていることです。
エキスパートに尋ねる
詳細、価格のお見積りについてお問い合わせください。Viaviのエキスパートがお客様のあらゆる質問にお答えします。