What is 5G Architecture?
5G leads the way towards disaggregated, flexible, and virtual RAN with new interfaces creating additional data access points.
The primary goal of previous mobile network generations was to offer fast, reliable mobile data services to network users. 5G has broadened this scope to offer a wide range of wireless services delivered to the end user across multiple access platforms and multi-layer networks.
5G creates a dynamic, coherent, and flexible framework of advanced technologies to support a variety of applications. 5G utilizes a more intelligent architecture, with Radio Access Networks (RANs) no longer constrained by base station proximity or complex infrastructure. 5G leads the way towards disaggregated, flexible, and virtual RAN with new interfaces creating additional data access points.

Services are provided via a common framework to network functions that are permitted to make use of them. Modularity, reusability, and self-containment of these network functions are additional design considerations for the 5G network architecture described by the 3GPP specifications.
5G Spectrum and Frequency
Multiple frequency ranges are now being dedicated to 5G new radio (NR). The portion of the radio spectrum with frequencies between 30 GHz and 300 GHz is known as the millimeter wave, since wavelengths range from 1-10 mm. Frequencies between 24 GHz and 100 GHz have been allocated to 5G in multiple regions worldwide.
- In addition to the millimeter wave, underutilized UHF frequencies between 300 MHz and 3 GHz and C-band frequencies between 3.7 and 3.98 GHz have also been repurposed for 5G.
The diversity of frequencies employed can be tailored to the unique application. Higher frequencies are characterized by higher bandwidth and shorter range.
Millimeter wave frequencies are ideal for densely populated areas, but ineffective for long distance communication.
- Within the various frequency bands dedicated to 5G, each carrier has begun to carve out their own individual portions of the 5G spectrum.
MEC
Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) is an important element of 5G architecture. MEC is an offshoot of cloud computing that brings applications from centralized data centers to the network edge, closer to end users and their devices. This essentially creates a shortcut in content delivery between the user and host, bypassing the long-distance network path that once separated them. This technology is not exclusive to 5G but is certainly integral to its efficiency.
- Characteristics of MEC include the low latency, high bandwidth, and real time access to RAN information that distinguish 5G architecture from its predecessors.
- 5G networks based on the 3GPP 5G specifications are an ideal environment for MEC deployment. These specifications define the enablers for edge computing, allowing MEC and 5G to collaboratively route traffic.
- Distribution of computing power enables the high volume of connected devices inherent to 5G deployment and the Internet of Things (IoT), in addition to the latency and bandwidth benefits.
- Convergence of RAN and core networks will require operators to leverage new approaches to network testing and validation.
NFV and 5G
Network function virtualization (NFV) decouples software from hardware by replacing various network functions such as firewalls, load balancers, and routers with virtualized instances running as software. This eliminates the need to invest in many expensive hardware elements and can also accelerate installation times, thereby providing revenue generating services to the customer faster.
NFV enables the 5G ecosystem by virtualizing appliances within the 5G network. This includes the network slicing technology that enables multiple virtual networks to run simultaneously. NFV addresses other 5G challenges through virtualized computing, storage, and network resources that are customized based on the applications and customer segments.
5G RAN Architecture
The concept of NFV extends to the RAN through the network dis-aggregation promoted by alliances such as O-RAN. Open RAN architecture eases the deployment of new RAN features and technology to scale by encouraging open interfaces and open-source development practices. This evolution increases flexibility and creates new opportunities for competition.
The O-RAN ALLIANCE objective is to allow multi-vendor deployment with off-the shelf hardware for improved inter-operability. Network dis-aggregation also allows more components of the network to be virtualized, providing a means to scale and improve user experience quickly as capacity grows. Virtualized RAN is essential for controlling hardware and software costs in the rapidly expanding ecosystem of IoT applications.
eCPRI
Network dis-aggregation with the functional split also brings other cost benefits, particularly with the introduction of new interfaces such as eCPRI. RF interfaces are not cost effective when testing large numbers of 5G carriers as the RF costs rapidly multiply. The original CPRI interface developed for 4G was vendor specific in many instances, which made it problematic for operators. eCPRI interfaces provide a more efficient solution as fewer interfaces can be used to test multiple 5G carriers. eCPRI has been designated as a standard interface for 5G O-RAN fronthaul elements such as the DU.
Network Slicing
A key ingredient for enabling the full potential of 5G architecture is network slicing.
This technology adds an extra dimension to the NFV domain by allowing multiple logical networks to run simultaneously on top of a shared physical network infrastructure. This capability supports 5G architecture by creating end-to-end virtual networks that include both networking and storage functions.
- Operators can effectively manage diverse 5G use cases with differing throughput, latency and availability demands by partitioning network resources to multiple users or “tenants”.
- Network slicing becomes extremely useful for applications like the IoT where the number of users may be extremely high, but the overall bandwidth demand is low.
- 5G verticals each have their own requirements, so network slicing is an important design consideration for 5G network architecture.
- Operating costs, resource management, and flexibility of network configurations can be optimized with the level of customization afforded by network slicing.
- Expedited trials for potential new 5G services and quicker time-to-market are also enabled by network slicing.
Beamforming
Another breakthrough technology integral to the success of 5G is beamforming. Conventional base stations transmit signals in multiple directions without regard to the position of targeted users or devices. Using multiple-input, multiple-output (MIMO) arrays featuring dozens of small antennas combined in a single formation, signal processing algorithms are used to determine the most efficient transmission path to each user. Individual packets can be sent in multiple directions then choreographed to reach the end user in a predetermined sequence.
With 5G data transmission occupying the millimeter wave, free space propagation loss, proportional to the smaller antenna size, and diffraction loss, inherent to higher frequencies and lack of wall penetration, are much greater. On the other hand, the smaller antenna size also enables much larger arrays to occupy the same physical space. With each of these smaller antennas potentially adjusting or reassigning beam direction several times per millisecond, massive beamforming to support the challenges of 5G bandwidth becomes more feasible. With a larger antenna density in the same physical space, narrower beams can be achieved with massive MIMO, providing high throughput and more effective user tracking.
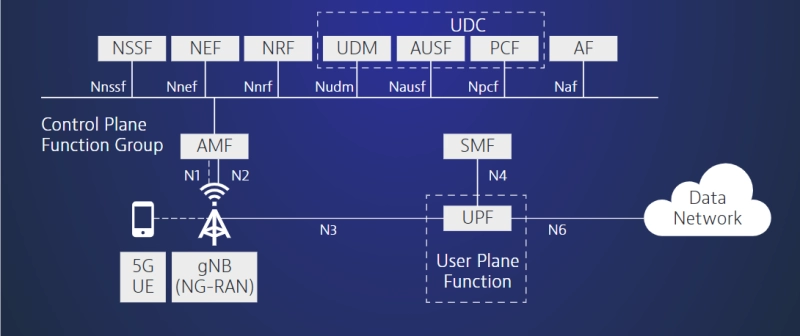
The 5G core network architecture is at the heart of the new 5G specification and enables the increased throughput demand that 5G must support. The new 5G core, as defined by 3GPP, utilizes cloud-aligned, service-based architecture (SBA) that spans across all 5G functions and interactions including authentication, security, session management and aggregation of traffic from end devices. The 5G core emphasizes NFV with virtualized software functions deployed using the MEC infrastructure that is central to 5G architectural principles.
Differences from 4G Architecture
Changes at the core level are among the myriad of architectural changes that accompany the shift from 4G to 5G, including the migration to millimeter wave, massive MIMO, network slicing, and essentially every other element of the diverse 5G ecosystem. The 4G Evolved Packet Core (EPC) is significantly different from the 5G core, with the 5G core leveraging virtualization and cloud native software design at unprecedented levels.
Among the other changes that differentiate the 5G core from its 4G predecessor are user plane function (UPF) to decouple packet gateway control and user plane functions, and access and mobility management function (AMF) to segregate session management functions from connection and mobility management tasks.
5G Architecture Options
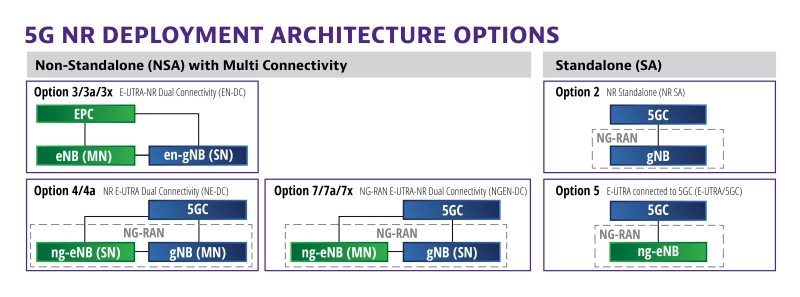
Bridging the gap between 4G and 5G requires incremental steps and a well-orchestrated game plan. Emblematic of this shift is the gradual transition from non- standalone mode to standalone mode 5G architecture options. The 5G non-standalone standard was finalized in late 2017 and utilizes existing LTE RAN and core networks as an anchor, with the addition of a 5G component carrier. Despite the reliance on 4G architecture, non-standalone mode increases bandwidth by tapping into millimeter wave frequencies.
5G standalone mode is essentially 5G deployment from the ground up with the new core architecture and full deployment of all 5G hardware, features, and functionality. As non-standalone mode gradually gives way to all new 5G mobile network architecture deployments, careful planning and implementation will make this transition seamless for the user base.
The infrastructure inherent to standalone 5G deployment requires a worldwide step function in 5G integration for various geographical regions. Technology leading regions such as North America, Asia, and Europe are ramping deployment quickly while other nations around the globe follow closely behind. Nearly 200 live 5G networks are already in service around the globe with the number of mobile 5G connections projected to exceed 2 billion by 2025.
The proximity of neighboring countries and a proliferation of carriers have made the rollout more challenging in Europe. Although adoption has lagged other regions, the European Commission has initiated a policy known as the Digital Compass which calls for 5G access in all populated areas by 2030.
Industrial nations such as China, Japan, and India are heavily invested in the practical as well as the financial implications of the 5G conversion. New antenna, infrastructure hardware, and software technologies create a bonanza for electronics and software design and manufacturing industries around the world, with speedy deployment being emphasized. The four largest telecom providers in India are rolling out 5G services following an August 2022 spectrum auction, and China is expected to have 3.64 million 5G base stations installed by 2025.
5G implementation brings tremendous performance benefits and diversity of applications through extensive use of cloud-based resources, virtualization, network slicing, and other emerging technologies. With these changes come new security risks and additional “attack surfaces” exposed within the 5G security architecture.
- 5G security practices build upon past mobile technology generations, yet the “trust model” has expanded with more players involved in the service delivery process.
- The IoT and user propagation create an exponentially higher number of endpoints with many of these traffic inputs no longer supervised by human hands.
- Improved 5G security features detailed by the 3GPP standards include unified authentication to decouple authentication from access points, and public key based encryption schemes to reduce the risk of metadata exploits.
- Continual monitoring and assessment of security effectiveness are essential as 5G critical performance nodes become increasingly virtualized.
- Best practices include end-to-end 5G network security monitoring encompassing the system architecture, devices, and apps.
Undoubtedly, 5G is delivering the exponential speed enhancement users have come to expect with each new generation of mobile networks, but speed is just the beginning. The changes to industries ranging from personal transportation to manufacturing and farming are so significant that many have dubbed 5G the next Industrial Revolution. At the heart of this paradigm shift is the multi-faceted 5G architecture, with MEC, NFV massive MIMO and a cloud-aligned, service-based core architecture working in concert to deliver the new wave of services. 5G test solutions designed to accommodate this architectural seed change will be the true enablers of the forthcoming 5G transition.
Learn about 5G VIAVI today!
Are you ready to take the next step with one of our 5G test products or solutions?
Complete one of the following forms to get going: